The ultimate guide to Bitcoin halving
When mining cryptocurrencies, we may encounter the process of halving. This is the usual case if you are interested in Bitcoin (BTC).
When Bitcoin halving occurs, it causes a change in the price of Bitcoin as well. These halvings are done in specific periods, and the reason behind the halvings is the limited capacity of Bitcoin mining.
As such, in order to understand the halving process of Bitcoin, you should first be aware of how Bitcoin mining is done.
What Is Mining?
The idea behind decentralized systems is that transactions that are done on the blockchain are verified collectively by other people. For these verifications to occur, computer nodes, or as we know as miners, solve advanced mathematical problems that sign the transaction with a public key as a form of verification.
After a transaction is verified, the block of information regarding the transaction is added to a chain of other blocks, consequently forming a blockchain. New blocks are added every 10 minutes.
In order for a computer node to verify a transaction, it requires technological costs, such as powerful graphic cards and electricity. But why would people pay for these costs just to verify transactions? Where is the benefit of mining?
After each transaction is verified, computer nodes (miners) responsible for the verification are rewarded free tokens or units of that cryptocurrency as an incentive to keep on mining. Hence, mining cryptocurrencies can be profitable if the amount mined is worth more than the cost.
When it comes to Bitcoin (BTC), 6.25 BTC are mined for each verification.
What Is Halving?
So what is halving? As the term suggests, halving is the process of dividing by two the amount that a cryptocurrency is mined. If Bitcoin mining capacity now is 6.25 BTC, then when Bitcoin is halved, it will be 3.125BTC. Additionally, Bitcoin has been halved before. In fact, Bitcoin has been halved three times ever since its release in 2009.
When Bitcoin was initially released, the amount of BTC that was mined was 50 BTC. The first Bitcoin halving occurred in 2012, and the amount rewarded to computer nodes was 25 BTC for each additional block of information added to the blockchain. In 2016, the second halving occurred, with the mining capacity halving to 12.5. In 2020, the third and latest halving occurred with a mining capacity of 6.25 BTC. The next Bitcoin halving is expected to occur in 2024.
In other words, this amount is halved every four years.
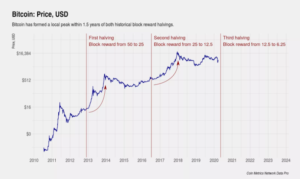
Logarithmic chart of Bitcoin (BTC) price after halving in 2012, 2016, and 2020. Source: Investopedia.com
Why Is Halving Done?
By now, you are probably wondering why the halving process exists. The answer to that is actually quite simple.
Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, have a limited amount of supply. To illustrate, Bitcoin has a limited supply capacity of 21 million BTC. Around 18 million BTC have already been mined and are in circulation.
If halving would not occur, Bitcoin’s limit would have been reached by now. Thus, since Bitcoin mining capacity is halved every four years, the next halving process is expected to be in 2024.
At this rate, Bitcoin’s supply limit would be achieved by the year 2140.
When Bitcoin is halved, the price of Bitcoin rises as well. The reason for this increase in price is because the demand for Bitcoins is high, and Bitcoin gets scarcer, causing the price to increase. Whenever demand exceeds supply, the price automatically rises to eliminate the shortage (laws of supply and demand).
However, looking at price patterns when Bitcoin was halved, whenever Bitcoin increased massively, it was followed by a big decline as well. That decline is yet to come in 2021, as the price has reached around $60,000 in March. Perhaps, BTC price might not decline at all.
According to Investopedia, this is how halving influences the price of Bitcoin:
The reward is halved → half the inflation → lower available supply → higher demand → higher price → miners incentive still remains, regardless of smaller rewards, as the value of Bitcoin is increased In the process.
All in all, halving occurs because the supply of a cryptocurrency (i.e. Bitcoin) is limited and people in charge of the Bitcoin network do not want the supply to run out any time soon.=
Effects Of Bitcoin Halving
As suggested, when Bitcoin halves, its price is affected as well as the demand for Bitcoins increases.
What is worth mentioning for Bitcoin halving is that mining becomes much more difficult and expensive. In fact, mining Bitcoins in 2021 can bring losses rather than profits. Because of this phenomenon, people who mine Bitcoins are more inclined to sell the Bitcoins they mined immediately in order to cover the large expenses. However, since Bitcoin halving implies an almost inflation-free currency, selling pressure also drops.
What Happens When The Last BTC Is Mined?
What happens when Bitcoin reaches its limit of 21 million by the year 2140?
Even though it is still a long way to go until 2140, when Bitcoin supplies its last ever BTC, miners can still verify transactions, even though there might not be any profit. Computer nodes can be compensated through transaction fees. However, it is difficult to say what can happen a year from now for a cryptocurrency, let alone a hundred years from now.
One thing is for sure. The halving process plays a vital role in determining the nature and future of a cryptocurrency.
Takeaways
- To understand halving, you should briefly understand the concept of mining.
- Mining is the process of verifying transactions done in the blockchain through computer nodes, which are involved in solving advanced mathematical operations. Whenever a new block of information is added to the blockchain, miners are rewarded free cryptocurrencies as an incentive to keep mining.
- Halving is the process of reducing the amount that a cryptocurrency is mined by half.
- Bitcoin halving occurs every four years. The latest Bitcoin halving was in 2020, and the amount of BTC mined for each additional block of information added to the blockchain is 6.25 BTC.
- Bitcoin halving occurs because Bitcoin has a limited supply of 21 million BTC. As of 2021, 18 million BTC have already been mined.
- Bitcoin halving affects the price of BTC, as well as an increase in demand.
- Bitcoin is expected to reach its limit in the year 2140, where no more BTC can be mined.