Explaining What is BFT? or Byzantine Fault Tolerance is not as easy as definition or meaning in the dictionary, so let’s dig into a little history.
For almost a decade after Bitcoin‘s founding, numerous other cryptocurrencies have been created, each with its own unique method. While each cryptocurrency has its own unique characteristics, the blockchain is a fundamental part of practically every one of them.
Blockchains are unsupervised digital ledgers that are updated by a decentralized computer network, with just a few notable exceptions. Therefore, the development of economic systems based on blockchain technology allows for the execution of public and trustworthy transactions without the involvement of third parties. There is a growing acceptance of cryptocurrency as an alternative to modern banking systems, which are highly trust-based.
Consensus achievement is the process by which the members of a network concur on the present state of the particular blockchain on a routine basis. While it is possible to obtain agreement over distributed networks, it is far from simple. As a result of this problem, the idea of Byzantine fault tolerance was born.
The Byzantine Fault Problem
The Byzantine Generals’ Problem is a theoretical issue that highlights how a number of Byzantine generals might struggle to communicate while deciding on their upcoming move. The issue implies that every general has his own troops and that each unit is spread out around the area. The generals must charge or retreat.
There is just one option for each general: either to assault or retreat. The choice of a general can not be reversed once they have made it. There must be a universal consensus among the generals as to what to do, and they must execute it coordinately.
One general may only contact the other by courier-delivered communications, causing various challenges. As a result, the core problem of the Byzantine Generals’ Problem is that the communications might be either stalled, damaged, or completely lost. Furthermore, even if a message is sent properly, any general may transmit a false message to mislead others, causing a complete failure.
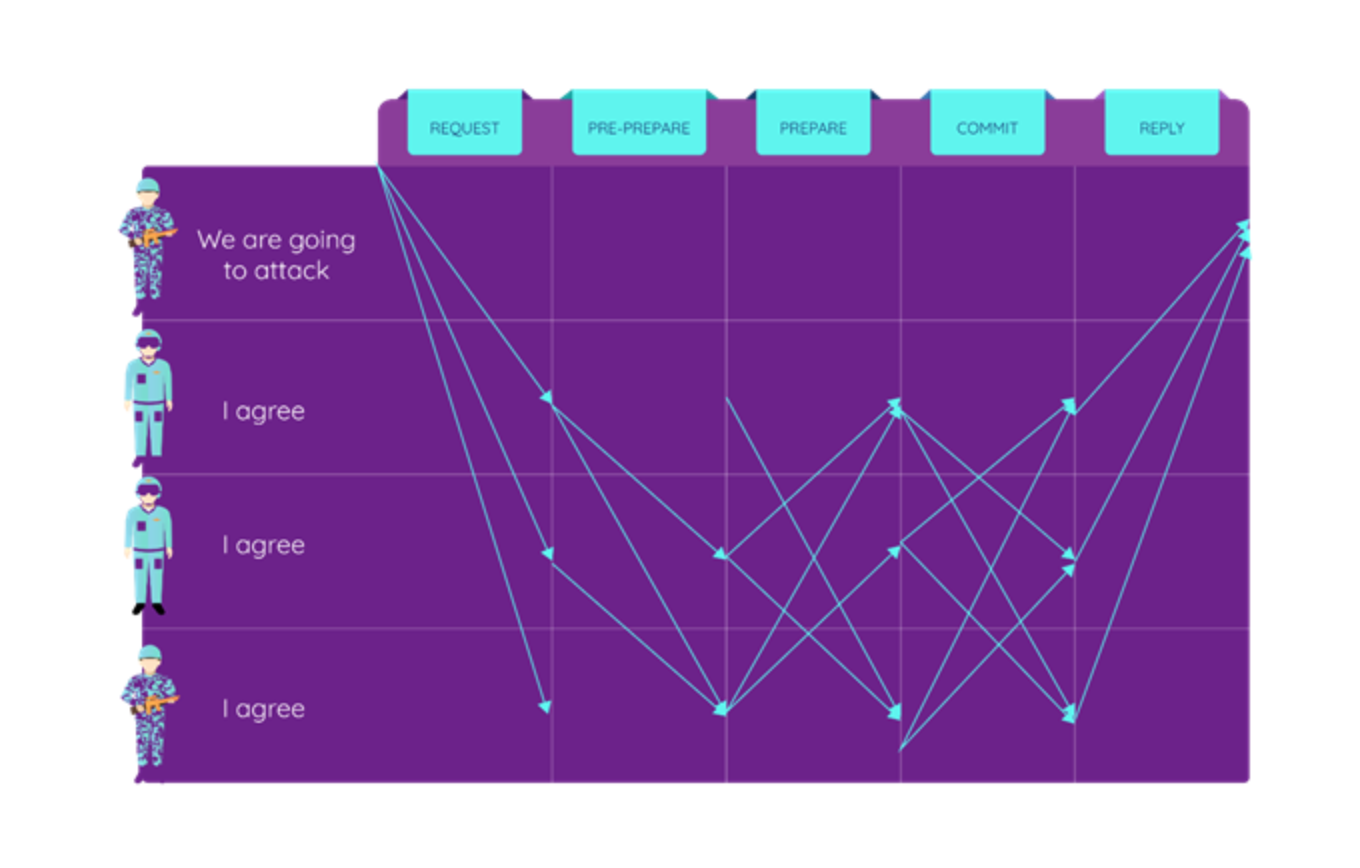
(The Byzantine General Dilemma illustrated. Source: Medium)
Every general symbolizes a network node in blockchains, and the nodes must achieve agreement on the system’s state. In other words, the majority of members in a decentralized system must agree and take the same action to prevent failure. At least 66% or more dependable and honest network nodes can establish consensus in these distributed systems.
How Does Byzantine Fault Tolerance Work?
Byzantine Fault Tolerance is the capacity of a computer network to remain functional even if some of its nodes malfunction or behave maliciously. Byzantine Fault Tolerance is significant in modern technology because it allows a system to operate even if some of its components fail. A computer system, such as that of an aircraft, must be able to function even if not all of its nodes are functioning. In order for blockchains to process crypto transactions, Byzantine Fault Tolerance is mandatory.
Cryptocurrency transactions are validated, processed, and recorded using the blockchain. There must be a consensus among the nodes before a transaction is completed. A consensus algorithm is a set of rules that all nodes in a blockchain network must follow in order to agree on transactions.
Counting on node votes and reaching an agreement by a large majority is the idea of an alternate approach to the problem. Which has the advantage of not needing procedures that are resource-intensive for the computer. The disadvantage of using this method is that it will only provide security against Byzantine Faults for as long as a sizeable majority of the nodes on the blockchain behave in a lawful manner.
Nodes in the Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) system are ensured to agree on the time and consensus of transactions in the network. That’s irrelevant to whether or not a third or more of the nodes are intentionally stalling transactions or manipulating the system in some other way to prevent the agreement from being reached.
What is BFT? – Advantages of BFT
First and foremost, it’s the ease and speed with which transactions may be completed. The agreement and timing of transactions are guaranteed in the Byzantine fault-tolerant (BFT) network. Therefore, it doesn’t matter how many nodes are deliberately blocking transactions or abusing the system to avoid agreement.
Transactions don’t need numerous verifications. When all of the nodes in the network reach a consensus over a bunch of transactions, the block is instantly verified. Because there are not many miners involved in the process of working out complicated calculations for each block of transactions. There isn’t a large need for a huge amount of computer power or energy consumption. Because of this, it is much better for the health of the environment.
This Byzantine Fault Tolerance method has a lower energy consumption than the PoW consensus mechanism. The Proof-of-Work mechanism requires a new PoW cycle for every new block. Crypto miners on the Bitcoin network gradually increase their power usage. Whereas other blockchains using BFT requires no expensive processing, resulting in a significant decrease in electrical energy use.
What is BFT? – Disadvantages of BFT
Nevertheless, there are a few drawbacks associated with putting BFT into practice. For instance, the BFT system can only be used in its traditional form when it is put to practical use. Because of this, you are only able to participate in limited consensus group sizes in order to prevent the excessive amounts of communication that are required among nodes.
In addition, the employment of digital signatures for the purpose of authenticating communications might raise questions over their potential inefficiency. Moreover, the security of the procedure is increased according to the number of nodes that apply it. And this does have an adverse effect on the flexibility as well as the bandwidth of the network.
The system is also vulnerable to cyberattacks and malfunctions if the majority of the network chooses to behave maliciously. A majority assault, also known as a 51% attack, takes place when a single individual or group of people obtains influence of more than 50% of a blockchain’s computing power. The most common method for doing this is to lease mining computer power from other third parties.
In addition to the obvious danger of the attacker illegally stealing assets or spending them, there is also the less obvious but probably more serious danger of the public’s faith in the blockchain system being severely damaged.
Why Does BFT Matter?
To the layman, the technicalities of BFT may seem to be of concern primarily to computer scientists and crypto enthusiasts. They are, to a degree. Moreover, Byzantine faults should no longer be a concern for consumers after a secure blockchain is established.
In the meanwhile, those who are interested in using blockchains for purposes other than financial transactions can educate themselves with BFT, which is still in the initial planning stages in many places. For certain blockchain applications, Bitcoin’s solution to the problem of Byzantine Fault may not be effective.
BFT is a critical component of a successful blockchain, and it may be applied in several methods. Choosing a method means considering the kind of blockchain ecosystem an organization seeks to build, as well as the goals that the community has.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it should be noted that it is plainly obvious that Byzantine Fault Tolerance plays an important part in the transformation of consensus-based systems. Applications using blockchain technology are gradually gaining steam across a variety of industries. Yet, there are plenty of issues that are coming to light in recent blockchain networks.
In light of this, it is essential to see BFT as an essential tool for ensuring that the system continues to operate correctly in spite of the presence of malicious actors. Because blockchain is open and transparent, it might attract unethical parties. Therefore, it is vital to have a solid understanding of consensus processes, including BFT.
TakeAways
- Since Bitcoin was created almost ten years ago, many other cryptocurrencies have been made, each with its own method.
- Consensus achievement is the process by which members of a network regularly agree on the current state of a blockchain.
- The Byzantine Generals’ Problem shows how Byzantine generals could struggle to communicate while planning their next move.
- Each cryptocurrency has a consensus algorithm that helps it reach at least some level of Byzantine Fault Tolerance.
- Byzantine Trench Tolerance is a computer network’s ability to operate despite malfunctioning or malicious nodes.
- A consensus algorithm is a set of rules that all nodes in a blockchain network must follow in order to agree on transactions.
- As blockchain technology continues to grow, so too will the processes employed to establish consensus.