A complete guide to mining, hash, and hash rate
If you have been trying to learn about cryptocurrencies and how they work, then you have probably encountered the process of mining and the concept of hash.
In order to understand the realm of cryptocurrencies, you need to understand what these terms entail because they play an important job in cryptocurrencies and their market. Mining, as the word suggests, is the process of obtaining cryptocurrencies by adding information to the blockchain and confirming transactions through miners (computer nodes).
Whenever a block of information is added to the blockchain, it contains a unique reference of numbers and letters, which is called a hash.
In order for a cryptocurrency to be mined, energy is required. The speed that a cryptocurrency is mined based on the energy it consumes is called the hash rate.
We will explore in detail how all mining, hash, and hash rates work.
What Is Mining?
Cryptocurrencies run in a decentralized manner, which means that no central authority runs a network. But if no one is in charge of regulating a network, how does that network work?
In decentralized systems, the power is shared among everyone who is a part of that cryptocurrency. Every transaction and service is verified collectively by people in a crypto network in order to make sure that that transaction or service is valid.
In order for a transaction to be verified, computer nodes (miners) are required to solve advanced mathematical problems. After those problems are solved, the transaction is signed by a public key, meaning that the transaction is valid.
After the verification occurs, the block of information is added to a chain of other blocks, forming a blockchain.
Blockchain is this virtual ledger that keeps track of all the information regarding transactions and services conducted in a cryptocurrency network.
But in order for miners to solve those advanced mathematical problems and verify transactions, powerful graphic cards and a vast amount of electricity are required.
But why would people voluntarily mine in a cryptocurrency network if mining means extra cost?
Actually, as an incentive to people who voluntarily mine to keep on mining, networks reward those miners with free cryptocurrencies for each block of information added to the blockchain.
The mining capacity is different for each cryptocurrency. Few cryptocurrencies go through the process of halving, which means that the amount that can be mined halves after a specific period.
So even though mining can be expensive, you can actually profit from the number of cryptocurrencies that you mine.
Unfortunately, there are very few cases when mining costs exceed the revenue from selling the cryptocurrencies that are mined, leading to temporary losses.
What Is Hash?
Each block of information added to the blockchain is unique. Every block of information has a form of identification. This identification is composed of 64 characters (numbers and letters). This reference number of 64 characters within the block of information added to the blockchain is known as a Hash block.
Each block of information in the blockchain also contains the algorithm for the previous hash block. Since each hash block is added on top of another hash block to form a chain, previous hashes cannot be altered, which actually makes a blockchain safer from hackers that want to manipulate its data.
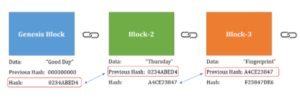
Hash blocks in a blockchain. Sources: Medium.com
A block of information contains the Merkle root, which is the mathematical way of making sure that information in the blockchain remains unchanged. If you want to verify information about a specific block (i.e. block #100) without having to check on its previous (block #99) or next block (block #101), you can simply check the block’s Merkle tree.
In order to find a unique number that is used as identification for a block of information, nonce (a number that can be used only once) – which is considered a lucky number and also known as ‘mining field’ – needs to be found. After nonce is found, the miner is rewarded for its contribution to find it.
After a unique hash is found (below the target), miners notify the network so that others update their information in the blockchain as well.
To conclude, the hash is the reference number of a block in the blockchain that makes the block unique.
What Is Hash Rate?
Now that you briefly know about the process of mining and hash blocks, it is important to understand what the Hash rate is.
Hash rate is the speed or processing capacity at which mining is being conducted in a blockchain. So the hash rate is a form of measurement for people to know the efficiency and productivity that mining in a cryptocurrency has.
So how to determine if mining a cryptocurrency is worth it or not?
Simply put, the higher the hash rate of a cryptocurrency, the more efficient is the mining process in that cryptocurrency. So if the hash rate reaches a higher number than it usually has, you should keep mining because the chances that you are rewarded from a blockchain become higher. It is a direct relation, so if the hash rate lowers, your chances for successfully mining lower as well.
The hash rate is measured in hashes per second (h/s). As per Paxful, Hash rate units are:
- 1 kilo hash per second (1 Kh/s) = one thousand hashes per second (1,000 h/s)
- 1 mega hash per second (1 Mh/s) = one million hashes per second (1,000,000 h/s)
- 1 giga hash per second (1 Gh/s) = one billion hashes per second (1,000,000,000 h/s)
- 1 tera hash per second (1 Th/s) = one trillion hashes per second (1,000,000,000,000 h/s)
- 1 peta hash per second (1 Ph/s) = one quadrillion hashes per second (1,000,000,000,000,000 h/s)
- 1 exa hash per second (1 Eh/s) = one quintillion hashes per second (1,000,000,000,000,000,000 h/s)
Hash rate is determined by the computing power of a miner, as well as the cryptocurrency itself.
Let’s take as an example Bitcoin, the world’s leading cryptocurrency. Since Bitcoin becomes scarcer day by day, people invest more money in their mining power, by buying and utilizing powerful graphic cards, as well as providing sufficient electricity to support the mining. The whole process of mining can be viewed as a competition on who has a more powerful console to mine Bitcoins since higher power means a higher hash rate; a higher hash rate means a higher chance of mining Bitcoins.
However, the more powerful a node is, the less likely are other nodes to successfully mine a Bitcoin. Consequently, nowadays it is very hard for people with simpler setups to successfully mine Bitcoins.
Other cryptocurrencies, fortunately, are more likely to have less competition: Anyone with a simple mining setup can successfully mine and make a profit from mining these other cryptocurrencies because their respective hash rates on their nodes are higher.
When it comes to energy consumption, it also depends on the power of the computer node and the cryptocurrency.
Powerful systems with advanced graphic cards have a higher success rate when mining cryptocurrencies, but the electricity costs are also higher. This is the usual case with application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) miners, which are powerful cryptocurrency miners.
With a low hash rate and high electricity costs, the likelihood of making a profit is very low. As suggested above, mining Bitcoin is not as profitable as it used to be in the past.
So is mining Bitcoin in 2021 profitable? The answer is still yes, even if the profits are much lower and the process is more complicated now.
Bitcoin Total Hash Rate throughout the years (2010-2021). Source: Blockchain.com
Takeaways
- Mining, hash, and hash rates are very important aspects of cryptocurrencies.
- Mining is the process of obtaining cryptocurrencies by adding information to the blockchain and confirming transactions through miners (computer nodes). Whenever a new block of information is added to the blockchain, miners are rewarded free cryptocurrencies as an incentive to keep mining.
- Hash is the reference number or identification of a block in the blockchain, which consists of 64 characters (numbers and letters).
- Each block of information contains its hash and the hash of the previous block.
- Hash rate is the speed or processing capacity at which mining is being conducted in a blockchain
- Hash rate depends on the computing power of the miners (i.e. powerful graphic cards), as well as the cryptocurrency itself.
- The higher the hash rate, the higher the success rate on mining. The lower the hash rate, the lower the success rate on mining.
- Hash rate is measured in hashes per second (h/s). Hash rate units are kilo hash per second (Kh/s), mega hash per second (Mh/s), giga hash per second (Gh/s)tera hash per second (Th/s), peta hash per second (Ph/s), and exa hash per second (Eh/s).
- A more powerful miner can lead to a higher hash rate, but also higher electricity costs. Because of this and the competition, mining cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin is not as profitable as it used to be.